Feb 3, 2023Types of differential costs. There are three types of differential costs, with the third being a hybrid of the first two. They are: Fixed cost. When a differential cost appears as a fixed cost, a business can assume that the expenses for each alternative remain the same regardless of the activities of the business.
Solved Answer these following questions: 1. Only variable | Chegg.com
All of the following costs would be found in a company’s accounting records except: A) sunk cost. B) opportunitycost. C) indirect costs. D) direct costs. … A sunk cost is: a cost that cannot be avoided because it has already been incurred. All of the following can be differential costs except: A) variable costs. B) sunk costs. C

Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
The new regulation renders the machine and the produced plastic bags obsolete, and the company cannot change the government’s decision. It is an expense that cannot be reversed or is a sunk cost. Applications of Differential Cost. Managers use differential cost in the following ways: 1. Determine the most profitable level of production and price

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
What is Differential Costing? Definition, Differential Cost, Formula and Example- The Investors Book Verified Answer for the question: [Solved] All of the following can be differential costs except: A) variable costs. B) sunk costs. C) opportunity costs. D) fixed costs.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
All Of The Following Can Be Differential Costs Except:
Verified Answer for the question: [Solved] All of the following can be differential costs except: A) variable costs. B) sunk costs. C) opportunity costs. D) fixed costs. Not all fixed costs are sunk—only those for which the cost has already been irrevocably incurred. A variable cost can be a sunk cost if it has already been incurred. 11-5 No. A variable cost is a cost that varies in total amount in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity. A differential cost is the
Manufacturing Cost Terms – ppt video online download
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Differential costs are always _____., Which of the following is always an irrelevant cost? a. Differential cost b. … Manufacturing costs include all of the following categories except _____. A. administrative costs B. direct labor c. direct materials d. manufacturing overhead. Portable Pressure & Temperature Calibrators | Druck

Source Image: bakerhughes.com
Download Image
Durability and physical characterization of anti-fogging solution for 3D-printed clear masks and face shields [PeerJ] Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Differential costs are always _____., Which of the following is always an irrelevant cost? a. Differential cost b. … Manufacturing costs include all of the following categories except _____. A. administrative costs B. direct labor c. direct materials d. manufacturing overhead.
![Durability and physical characterization of anti-fogging solution for 3D-printed clear masks and face shields [PeerJ]](https://dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net/2023/matsci-30/1/fig-1-full.png)
Source Image: peerj.com
Download Image
Solved Answer these following questions: 1. Only variable | Chegg.com Feb 3, 2023Types of differential costs. There are three types of differential costs, with the third being a hybrid of the first two. They are: Fixed cost. When a differential cost appears as a fixed cost, a business can assume that the expenses for each alternative remain the same regardless of the activities of the business.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
What is Differential Costing? Definition, Differential Cost, Formula and Example- The Investors Book The new regulation renders the machine and the produced plastic bags obsolete, and the company cannot change the government’s decision. It is an expense that cannot be reversed or is a sunk cost. Applications of Differential Cost. Managers use differential cost in the following ways: 1. Determine the most profitable level of production and price
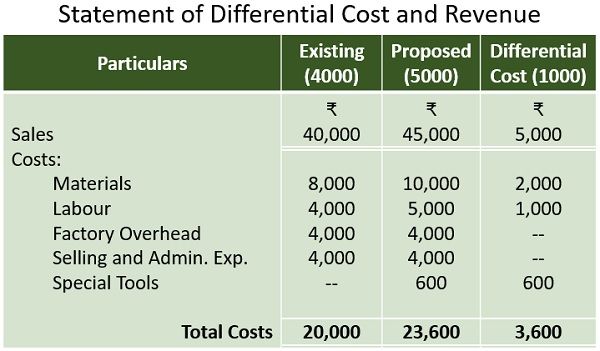
Source Image: theinvestorsbook.com
Download Image
EQ vs IQ: How They Differ, Which Is More Important? Key Takeaways Differential costs, sometimes called incremental, are the overall costs incurred while choosing between several options. They are the expenses incurred by selecting one course of action over another. By determining which choice is most likely to result in larger earnings, they aid in profit maximization.

Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
Differential, opportunity and sunk costs – explanation and examples | Accounting For Management Verified Answer for the question: [Solved] All of the following can be differential costs except: A) variable costs. B) sunk costs. C) opportunity costs. D) fixed costs.
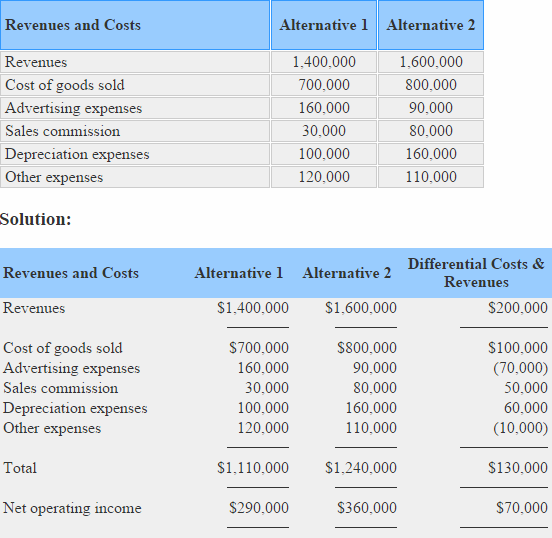
Source Image: accountingformanagement.org
Download Image
Ergonomic Mesh Back Office Chair | Diffrient Smart | Humanscale Not all fixed costs are sunk—only those for which the cost has already been irrevocably incurred. A variable cost can be a sunk cost if it has already been incurred. 11-5 No. A variable cost is a cost that varies in total amount in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity. A differential cost is the

Source Image: humanscale.com
Download Image
Durability and physical characterization of anti-fogging solution for 3D-printed clear masks and face shields [PeerJ]
Ergonomic Mesh Back Office Chair | Diffrient Smart | Humanscale All of the following costs would be found in a company’s accounting records except: A) sunk cost. B) opportunitycost. C) indirect costs. D) direct costs. … A sunk cost is: a cost that cannot be avoided because it has already been incurred. All of the following can be differential costs except: A) variable costs. B) sunk costs. C
What is Differential Costing? Definition, Differential Cost, Formula and Example- The Investors Book Differential, opportunity and sunk costs – explanation and examples | Accounting For Management Key Takeaways Differential costs, sometimes called incremental, are the overall costs incurred while choosing between several options. They are the expenses incurred by selecting one course of action over another. By determining which choice is most likely to result in larger earnings, they aid in profit maximization.